How Long Does It Take for Fried Chicken to Digest? Fried chicken is a beloved comfort food worldwide. Its crispy, golden exterior and juicy interior make it a favorite for many. However, when it comes to digestion, this indulgent dish can pose significant challenges for the body. Understanding how long it takes for fried chicken to digest involves delving into the complexities of the digestive process, the unique composition of fried chicken, and the various factors that can influence digestion times.
This comprehensive article provides an in-depth look at how the body processes fried chicken, including the physiological mechanisms involved, the estimated digestion timeline, and practical tips to improve digestive health after consuming this high-fat meal.
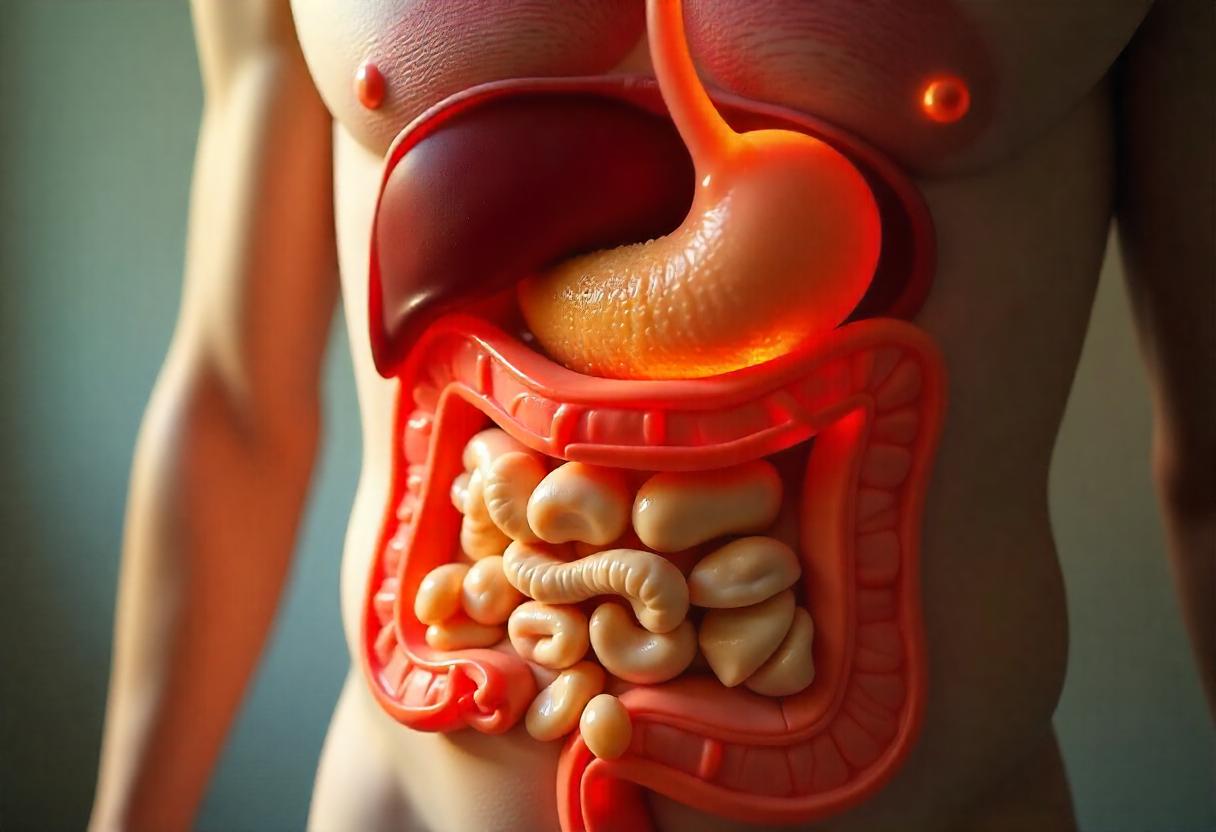
The Digestive Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Digestion is a complex physiological process designed to break down food into smaller molecules that the body can absorb and use for energy, growth, and repair. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the digestive stages, particularly focusing on how the body handles fried chicken:
1. Chewing and Saliva Enzymes
Digestion begins in the mouth. Chewing (mastication) breaks down fried chicken into smaller, manageable pieces. This mechanical process is critical for efficient digestion, as smaller food particles are easier to process further down the digestive tract. At the same time, saliva mixes with the food, introducing enzymes like amylase that begin breaking down carbohydrates in the chicken’s breading.
- Time Spent: 5-10 minutes
- Key Enzymes: Amylase (carbohydrate digestion starts here).
2. Journey Through the Esophagus
After swallowing, the chewed food travels down the esophagus through a process called peristalsis—wave-like muscular contractions that move food to the stomach. While this is a short journey, it plays a critical role in ensuring that food reaches the stomach intact and ready for further breakdown.
- Time Spent: Less than 10 seconds.
3. Stomach Digestion
The stomach is where the real work begins. Gastric juices, including hydrochloric acid and enzymes like pepsin, begin breaking down the proteins in fried chicken. The breading and oils, however, pose additional challenges. While proteins start to denature and break into smaller peptides, fats largely remain intact in this phase, waiting for bile and pancreatic enzymes in the small intestine.
- Time Spent: 2-4 hours.
- Key Enzymes: Pepsin (protein digestion).
4. Small Intestine Absorption
The small intestine is the primary site of digestion and nutrient absorption. Here, bile from the gallbladder emulsifies the fats in fried chicken, breaking them into smaller droplets that pancreatic enzymes (like lipase) can effectively process. Proteins are broken into amino acids, and carbohydrates are reduced to simple sugars like glucose. Nutrients are then absorbed into the bloodstream through the intestinal walls.
- Time Spent: 4-6 hours.
- Key Processes: Fat emulsification by bile; nutrient absorption.
5. Large Intestine Processing
What remains after the small intestine is indigestible fiber, water, and waste products. These pass into the large intestine, where water and electrolytes are absorbed. The gut microbiota ferments undigested materials, producing gases and short-chain fatty acids that may provide additional energy.
- Time Spent: 10-24 hours.
- Key Role: Fermentation of undigested remnants; waste formation.
Estimated Total Digestion Time for Fried Chicken

Considering all these stages, the total time it takes to digest fried chicken can vary widely, depending on individual factors. On average, it takes:
- 12 to 48 hours for fried chicken to be fully processed and eliminated from the body.
This variability is influenced by factors such as metabolism, age, health conditions, portion size, and accompanying foods or beverages.
Nutritional Composition of Fried Chicken
Fried chicken’s digestion is influenced by its nutritional profile, which includes high levels of fat, moderate protein, and carbohydrates from the breading. Here’s an approximate breakdown for a standard 100-gram serving:
- Calories: 260-300 kcal
- Protein: 16-20 grams
- Fat: 15-20 grams
- Carbohydrates: 8-12 grams
- Fiber: 0-1 gram
The high fat content, in particular, plays a significant role in slowing digestion, as fats take longer to break down and absorb compared to carbohydrates or proteins.
Factors That Influence Fried Chicken Digestion
1. Fat Content
The oils used in frying significantly increase the fat content of the chicken. Fats are the slowest macronutrient to digest because they require emulsification by bile and enzymatic breakdown by lipase. This adds hours to the digestion timeline.
2. Cooking Methods and Ingredients
The type of oil used for frying, the thickness of the breading, and the presence of spices or seasonings can all impact digestion. Oils high in trans fats or saturated fats are harder for the body to process.
3. Portion Size
Larger portions of fried chicken overload the digestive system, leading to longer digestion times. A single drumstick will digest faster than a full plate of chicken wings or thighs.
4. Age and Metabolism
Younger individuals with faster metabolisms typically digest food more quickly. Conversely, older adults may experience slower digestion due to reduced metabolic rates and decreased digestive enzyme production.
5. Overall Health
Conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), gallbladder removal, or lactose intolerance (from dairy-based coatings) can significantly delay digestion. Additionally, dehydration or a lack of physical activity may contribute to slower gastrointestinal motility.
Common Digestive Challenges with Fried Chicken

1. Heartburn and Acid Reflux
The high fat content in fried chicken can relax the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), allowing stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus, causing heartburn or acid reflux.
2. Bloating and Indigestion
Overeating fried chicken can lead to bloating, gas, and general discomfort. The body struggles to break down large quantities of fats and proteins simultaneously.
3. Gallbladder Strain
The gallbladder plays a critical role in emulsifying fats with bile. Consuming fatty meals like fried chicken puts extra strain on this organ, which may cause discomfort or pain in individuals with gallbladder issues.
4. Weight Gain and Long-Term Health Risks
Frequent consumption of fried chicken can contribute to weight gain, high cholesterol levels, and other long-term health risks, such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
Tips to Improve Digestion After Eating Fried Chicken
1. Drink Plenty of Water
Hydration aids the digestive process by helping break down food and ensuring smooth movement through the intestines. Avoid sugary or carbonated beverages, which can exacerbate bloating.
2. Opt for Smaller Portions
Eating smaller portions reduces the burden on your digestive system. Pair your fried chicken with lighter, fiber-rich sides like steamed vegetables or salads.
3. Stay Active
Engage in light physical activity, such as walking, after a meal. This helps stimulate peristalsis, the muscular contractions that move food through the digestive tract.
4. Incorporate Digestive Aids
Consider taking digestive enzymes or probiotics to support gut health. These can help break down fats and proteins more efficiently.
5. Eat Slowly and Mindfully
Chewing thoroughly and eating at a slower pace allows your digestive system to keep up with the intake. This reduces the risk of overeating and promotes better digestion.
Healthier Alternatives to Traditional Fried Chicken

For those who love fried chicken but want to avoid its digestive challenges, consider these healthier alternatives:
- Air-Fried Chicken: Air fryers use minimal oil, resulting in a lower fat content while maintaining crispiness.
- Grilled Chicken: Grilling eliminates the need for oil, making it a leaner option.
- Oven-Baked Chicken: Baking provides a similar texture and flavor without the high-fat content of frying.
- Coating with Whole-Grain Breading: Using whole-grain breading adds fiber, which aids digestion and improves nutritional value.
Frequently Asked Questions Of How Long Does It Take for Fried Chicken to Digest?
1. Can eating fried chicken cause stomach pain?
Yes, the high fat content can slow digestion, leading to discomfort, bloating, or indigestion in some individuals.
2. Is fried chicken hard to digest for everyone?
While most people can digest fried chicken, factors like portion size, individual health conditions, and cooking methods can make it more challenging for some.
3. How can I make fried chicken easier to digest?
Pair it with fiber-rich sides, drink plenty of water, and eat in moderation to ease digestion.
Conclusion
Fried chicken is undeniably delicious, but its digestion requires significant effort from the body due to its high fat and protein content. On average, it takes 12 to 48 hours to fully process and eliminate fried chicken. By understanding the digestive process and adopting healthier habits, you can minimize the potential discomfort associated with consuming this popular dish.

Daniel, a seasoned author with 8 years of expertise in SEO, brings a delectable blend of culinary flair and digital finesse to the food niche on his website.