Food poisoning is a common illness caused by consuming contaminated food or beverages. Bacteria, viruses, parasites, or toxins present in the food can lead to various symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. It can occur from eating at restaurants, consuming improperly cooked food, or mishandling food during preparation.
Imagine enjoying a delicious meal at your favorite restaurant, only to find yourself doubled over in pain hours later. This scenario is all too real for many who experience food poisoning. Whether it’s a mild case that resolves quickly or a severe illness requiring medical attention, food poisoning can disrupt your life and leave you feeling miserable.
Preventing food poisoning involves practicing proper food safety measures such as washing hands before cooking, avoiding cross-contamination, and ensuring food is cooked to the appropriate temperature. By being vigilant about food hygiene and handling, you can reduce the risk of falling victim to this unpleasant condition. If you suspect you have food poisoning, it’s essential to stay hydrated and seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen. Stay informed and stay safe to enjoy your meals without worry.
How you get food poisoning
Food poisoning happens when you eat food or drink that has harmful stuff in it like bacteria, viruses, parasites, or toxins. This can make you sick. It usually comes from food that’s not cooked enough, fruits and veggies that haven’t been washed, mixing raw and cooked foods, or eating food that’s been sitting out for too long.
Symptoms of food poisoning include feeling sick, throwing up, having diarrhea, stomach pains, and having a fever. To avoid getting sick, it is important to handle food safely. This means washing your hands and surfaces often, cooking food properly, and keeping perishable items in the fridge. If you think, you have food poisoning, drink plenty of water and get medical help if you are still feeling bad.
What are the 1st signs of food poisoning?
First signs of food poisoning are often subtle and can mimic common stomach discomfort. You may experience mild nausea, which can be mistaken for general indigestion. Additionally, some may notice slight stomach cramps or a feeling of fullness after eating.
As food poisoning progresses, symptoms may escalate to include vomiting and diarrhea. These symptoms usually develop within a few hours to a few days after consuming contaminated food. It’s essential to stay hydrated and seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen.
How to know if you have food poisoning
If you suspect food poisoning, look out for symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach cramps, and fever. These signs typically appear soon after eating contaminated food or drinks, ranging from a few hours to a few days. It is crucial to stay hydrated and monitor your symptoms closely. If they persist or worsen, seek medical help promptly. Reflecting on recent food intake can also help pinpoint the source of contamination.
What to do for mild food poisoning
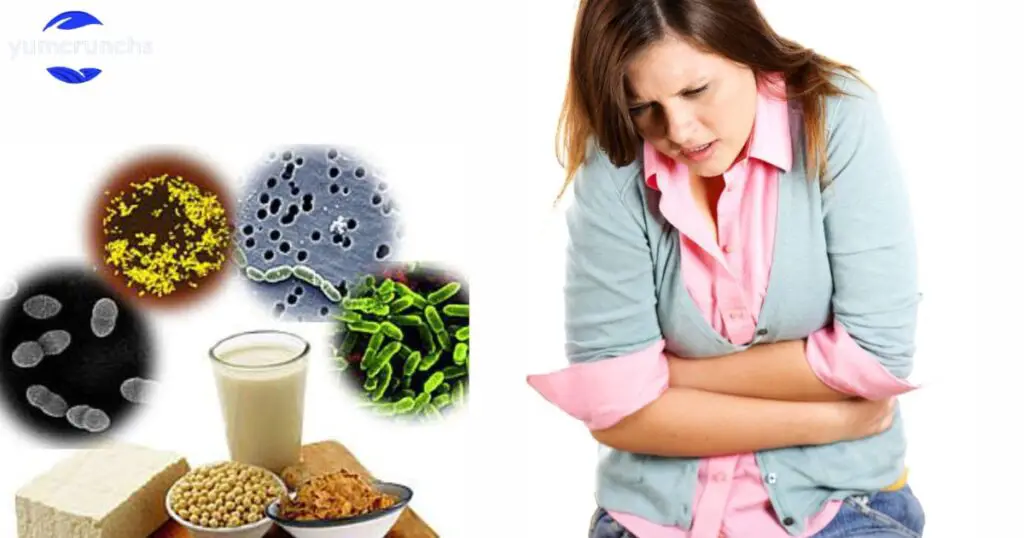

If you are experiencing mild food poisoning, there are a few steps you can take to help ease your symptoms and recover more quickly. Firstly, it is important to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water or clear fluids like broth or electrolyte drinks to replace lost fluids and prevent dehydration. Avoid solid foods for a little while to give your stomach a chance to settle. When you do start eating again, opt for bland, easy-to-digest foods like toast, rice, bananas, or plain crackers. Resting and allowing your body time to recover is also crucial, so take it easy and avoid strenuous activity until you are feeling better.
In addition to these self-care measures, if your symptoms persist or worsen, it is important to seek medical attention. Severe cases of food poisoning may require medical treatment or even hospitalization, especially if you are experiencing persistent vomiting, diarrhea, high fever, or signs of dehydration such as dizziness or decreased urination. Your doctor can guide managing your symptoms and may recommend certain medications to help alleviate discomfort or prevent complications. How Do You Use The FIFO Method to Restock Food? Overall, listening to your body, staying hydrated, and getting plenty of rest are key to recovering from mild food poisoning.
Causes
- Bacteria like Salmonella and E. coli contaminate food.
- Viruses such as norovirus spread through contaminated food.
- Parasites like Giardia can infect food and cause illness.
- Toxins produced by bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus in food can lead to poisoning.
- Improper food handling and storage can allow bacteria to multiply.
- Eating undercooked meats or raw eggs increases the risk of foodborne illness.
- Cross-contamination from raw meat to other foods can cause food poisoning.
- Consuming unpasteurized dairy products can lead to bacterial infections.
- Shellfish harvested from contaminated waters can carry harmful bacteria or toxins.
- Food prepared in unsanitary conditions can harbor pathogens that cause food poisoning
Symptoms

| Symptom | Meaning | Count |
| Nausea | The sensation of coldness and shivering | 1 |
| Vomiting | Forceful expulsion of stomach contents through the mouth | 1 |
| Diarrhea | Loose, watery stools | 1 |
| Abdominal pain | Pain or discomfort in the abdomen | 1 |
| Fever | Elevated body temperature | 1 |
| Headache | Pain in the head | 1 |
| Weakness | Lack of physical strength | 1 |
| Fatigue | Extreme tiredness | 1 |
| Muscle aches | Pain or discomfort in muscles | 1 |
| Dehydration | Excessive loss of body fluids | 1 |
| Loss of appetite | Reduced desire to eat | 1 |
| Chills | Sensation of coldness and shivering | 1 |
| Dizziness | Feeling lightheaded or unsteady | 1 |
| Watery stools | Loose, liquid-like bowel movements | 1 |
| Stomach cramps | Pain or discomfort in the stomach | 1 |
| Increased heart rate | Faster heartbeat than normal | 1 |
| Sensitivity to light | Increased sensitivity to light | 1 |
| Blurred vision | Loss of sharpness of vision | 1 |
| Confusion | Disorientation or mental fog | 1 |
| Difficulty breathing | Trouble taking in enough air | 1 |
Exams and Tests
When food poisoning is suspected, healthcare providers may conduct various exams and tests to identify the culprit. Firstly, a physical examination will be performed to assess symptoms like vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Doctors may also inquire about recent food consumption and any known outbreaks. What to Eat After Food Poisoning? Following this, stool samples may be collected to detect pathogens like bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Blood tests might also be conducted to check for signs of infection or dehydration.
Additionally, imaging tests such as X-rays or CT scans may be utilized in severe cases to assess organ damage or complications. These exams and tests play a crucial role in diagnosing food poisoning, enabling prompt treatment to alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications. Early detection helps in managing the condition effectively and ensures a quicker recovery for the affected individual.
Treatment
Treatment for food poisoning typically involves addressing symptoms and replenishing lost fluids. If you suspect food poisoning, it is essential to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water or oral rehydration solutions. Over-the-counter medications like antidiarrheals can help alleviate symptoms like diarrhea and stomach cramps. Resting and avoiding solid foods for a while can also aid recovery. In severe cases, especially if symptoms persist or worsen, seeking medical attention is crucial. A healthcare professional may prescribe antibiotics or recommend hospitalization to manage severe dehydration or complications.
Prevention is key to avoiding food poisoning in the first place. Practicing proper food handling and storage techniques can reduce the risk of contamination. Cook foods thoroughly, separate raw meats from other foods, and refrigerate perishable items promptly. When dining out, choose reputable establishments with good hygiene practices. By being vigilant about food safety, you can lower the chances of experiencing food poisoning and enjoy meals without worry.
Possible Complications
Food poisoning can lead to various complications that can affect your health. Firstly, dehydration is a common complication, as vomiting and diarrhea can lead to a significant loss of fluids and electrolytes from the body. It is essential to replenish fluids to prevent dehydration, especially in vulnerable groups like children and the elderly.
Secondly, certain types of food poisoning can cause severe complications such as kidney failure, nerve damage, or even death in rare cases. For instance, botulism, a rare but serious form of food poisoning caused by the bacteria Clostridium botulinum, can lead to paralysis and respiratory failure if not treated promptly. Therefore, it is crucial to seek medical attention if you suspect food poisoning to prevent any potential complications.
When to Contact a Medical Professional

Food poisoning can bring about uncomfortable symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach cramps. Usually, these symptoms resolve on their own within a few days. However, it is crucial to know when to reach out to a medical professional. If symptoms persist for more than 48 hours, if there’s blood in vomit or stool, if dehydration becomes severe, or if there are signs of high fever or difficulty breathing, it’s time to contact a medical professional promptly.
In these situations, seeking medical attention can help prevent complications and ensure proper treatment. Medical professionals can assess the severity of the condition, provide necessary medications, and offer guidance on managing symptoms and staying hydrated. Do not hesitate to contact a healthcare provider if food poisoning symptoms worsen or if there are any concerns about overall well-being.
How long does food poisoning last?
Food poisoning typically lasts for only a few minutes. Once you feel the initial discomfort, it quickly passes within half an hour. It’s like a brief hiccup in your digestive system, easily forgotten once it’s over.
However, in rare cases, food poisoning can linger for weeks. It can become a prolonged illness that requires extensive medical attention. This is why it’s crucial to seek medical help immediately if you suspect you have food poisoning, to prevent any potential complications.
Serious Health Problems and Long-Term Effects of Food Poisoning
- Chronic kidney disease can result from severe cases of food poisoning.
- Guillain-Barré syndrome, a rare neurological disorder, may occur after certain types of foodborne illnesses.
- Reactive arthritis, causing joint pain and inflammation, can develop as a long-term effect.
- Hepatitis, a liver inflammation, might be triggered by certain foodborne pathogens.
- Hemolytic uremic syndrome, a condition affecting blood vessels and kidneys, can arise from foodborne bacteria like E. coli.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms may persist long after the initial bout of food poisoning.
- Increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes can be associated with severe foodborne infections.
- Can food poisoning harm fetus?
Can food poisoning harm fetus?
Food poisoning during pregnancy can be extremely harmful to the fetus. The toxins from contaminated food can easily cross the placenta, affecting the baby’s development and causing serious health issues. In severe cases, it can lead to miscarriage or stillbirth, putting both the mother and the baby at risk.
It’s essential for pregnant women to be cautious about the food they consume to prevent food poisoning. Avoiding raw or undercooked meat, unpasteurized dairy products, and unwashed fruits and vegetables can significantly reduce the risk. Additionally, practicing proper food hygiene, such as washing hands and cooking surfaces thoroughly, can help protect both mother and baby from the dangers of foodborne illnesses.
Frequently Asked Questions
how soon after food poisoning do you vomit
Vomiting typically occurs within 6 to 24 hours after consuming contaminated food causing food poisoning.
food poisoning bacteria
Common food poisoning bacteria include Salmonella, E. coli, Campylobacter, Listeria, and Clostridium perfringens.
how long does food poisoning last in adults
Food poisoning in adults usually lasts from a few hours to a few days, varying based on the type of contaminant and individual health factors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, food poisoning is a serious concern that affects countless individuals every year. From contaminated ingredients to improper food handling, numerous factors can contribute to this widespread issue. It is essential to remain vigilant about food safety in both our homes and when dining out.
As we reflect on the various causes and symptoms of food poisoning, it is natural to wonder about the best ways to protect our loved ones and ourselves. Whether it is ensuring proper cooking temperatures, practicing good hygiene in the kitchen, or staying informed about food recalls, there are steps we can take to minimize the risk.
Ultimately, understanding the importance of food safety is key to preventing instances of food poisoning. By staying informed and implementing precautionary measures, we can safeguard our health and well-being. As you consider the information presented, what steps will you take to prioritize food safety in your daily life?

Daniel, a seasoned author with 8 years of expertise in SEO, brings a delectable blend of culinary flair and digital finesse to the food niche on his website.



